Fertilizer for crops plays an essential role in modern agricultural practices as it provides essential nutrients that all plants must demand in order to establish a strong, healthy, and productive life form. Fertilizer for crops, like the nutrients found, must achieve the best balance of nutrients for a maximum crop yield.
Nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium along with secondary nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur help farmers fulfill the specific needs of different crops. Using the correct fertilizer for crops can improve crop health, increase soil fertility, and increase productivity on the farm.
Selecting fertilizers for crops and applying them at various stages of growth and development can help farmers maximize production. In an ideal world of fertilization, every crop harvest can be bigger, more nutritious, and higher profit-making.
Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Fertilizers for Crops in Modern Agriculture
In contemporary agriculture, fertilizer is a key component of higher crop yields, better produce quality, and sustainability of soil health. Fertilizers replenish nutrients in the soil that crops deplete, crucial to profits for modern agriculture.
Without fertilizers, soil will be depleted, and plants will be negatively impacted by poor harvests. Applying targeted fertilizers, farmers can offer their crops nutrients at every point in their growing life.
Importance of Fertilizer for Crops and Farm Profitability
Fertilizers help provide an increase in crop yield, so farming becomes more profitable and sustainable. If farmers practice balanced fertilization, plants will grow more rapidly, tolerate disease better, and produce higher quality fruits and vegetables.
Key Points:
- Fertilizer means more pounds of crop per acre, and more farm income.
- Healthy, well-fed crops need fewer pesticides and treatments.
- Properly fertilized crops increase the market value partly because of better size, color and taste.
- Fertilizers lower the risk of crop loss due to nutrient deficiency.
How Fertilizers Support Plant Nutrition and Soil Enrichment
Fertilizers provide a source for the primary nutrients, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, as well as secondary and micronutrients needed by plants. This helps ensure that plants are fully nourished for root growth, flowering and fruiting.
Takeaways:
- Potato fertilizer improves size and quality of tubers due to a balanced supply of potassium and phosphorus.
- Corn fertilizer has nitrogen for rapid stalk growth and ear development.
- Pumpkin fertilizer improved overall vine growth and larger fruit due to higher potassium levels.
- Cucumber fertilizer supports luxuriant foliage and continuous flowering for better yields.
- Fertilizers thus maintain soil fertility and provide nutrients in a reasonably balanced configuration over growing seasons.
The Science Behind Fertilizer Application and Crop Productivity
The use of fertilizer for crops has a basis in plant science. The plant nutrients fertilizers supply are nutrients that plants extract from the soil during their productive growth cycle. As plants absorb nutrients, they process those nutrients into energy that builds roots, leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. Fertilization is essential to replenish depleted soil and to produce features of continuous, productive harvests. Fertilization is also essential for maintaining soil health, even on soils that are considered highly fertile. Without fertilization, or with a poorly designed fertilization plan, even the most fertile soils will become increasingly unproductive over time. When farmers understand the roles of fertilizers, they can significantly improve the quality of crops, consistently maintain crop quality, and achieve greater yields.
How Fertilizers for Crops Work to Boost Growth
Fertilizers enhance the natural growth cycle of plants by supplying the three basic and essential nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Each of the three macronutrients performs functions that are important for plant growth and development.
Functions of the Major Essential Nutrients:
- Nitrogen is important for supporting leaf growth and building a strong stalk, especially for crops like corn where nitrogen fertilizer will be used.
- Phosphorus contributes to root formation and flowering, which is important for crops like pumpkin fertilizer for example, and potato fertilizer.
- Potassium promotes disease resistance and fruit size, which is important for cucumber fertilizer and crops that fruit.
Provided that fertilizers are applied correctly, fertilizers can create the perfect balance of nutrients for vigorous, healthy, and productive plants.
Proper Fertilizer Application Techniques for Different Crops
Different crops require specific methods of fertilizer application to ensure nutrients reach the rght part of the plant
Best Practices for Application:
- Broadcasting is suggested for overall nutrient coverage on large fields.
- Side-dressing is suggested for row crops such as corn and potato fertilizer application.
- Drip irrigation or fertigation is suggested for precision feeding, proper for cucumber fertilizer and pumpkin fertilizer.
- Foliar feeding is suggested for fast correction of deficiencies in specialty vegetables and fruits.
Each application method ensures that crop fertilizers are used efficiently and maximize plant uptake while reducing waste.
The Impact of Balanced Fertilization on Soil Health
Balanced fertilization not only helps crops but also builds soil for the long-term. Imbalanced fertilization, or simply over-application, can adversely affect soil structure and doing it wrong harms the microbial life in the soil. Here are the soil health benefits of balanced fertilization:
- Replenishes the nutrients that your intensive cropping has taken out.
- Supports the helpful microbes that naturally put back nutrients into the soil.
- When properly managed, it stops leaching and runoff of a crop nutrient.
- Provides balanced nutrients for crops programs that insure continuous productivity for future generations.
Types of Fertilizers for Crops: Which One is Right for You? 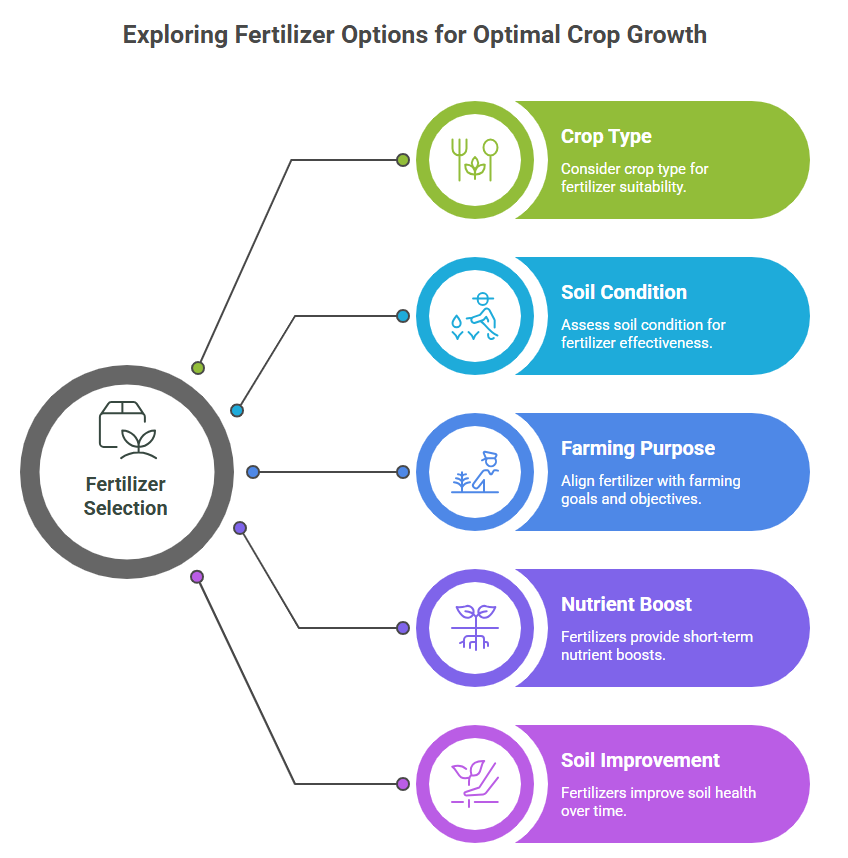
Selecting the appropriate fertilizer for crops takes into account the type of crops grown, the soil condition, and farming purpose. Different fertilizers provide various benefits - short-term nutrient boosts, longer-term soil improvement, or something in between. Knowing what options you have is vital to determine the best option and provide the best food for healthy plants and your maximum yield.
Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers for Crops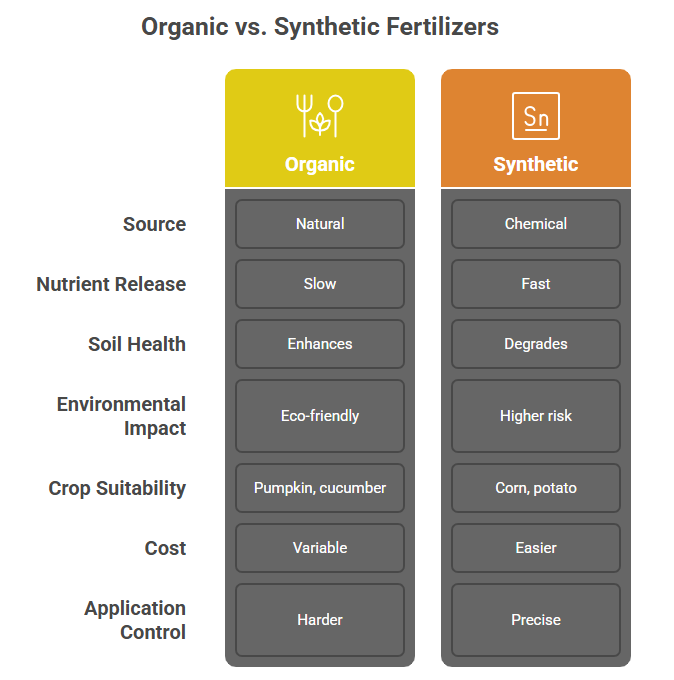
Liquid, Granular & Slow-Release Fertilizer Options
An application form has a significant impact on nutrient delivery for crop fertilizer.
Liquid Fertilizers:
- They are quickly absorbed by the root system of plants.
- They are well-suited for fertigation and foliar feeding (especially for cucumber fertilizer applications).
- They can be used to overcome an immediate nutrient deficiency.
Granular Fertilizers:
- When granular fertilizers are applied, they will be evenly spread for complete, uniform enrichment of the soil.
- Best when doing bulk applications of potato fertilizer and corn fertilizer.
Slow-Release Fertilizers:
- They release their nutrients slowly over a period of weeks or months.
- Requires less need for the frequent application of fertilizers.
- Accumulation of soil fertility over the years for our fruiting crops, such as pumpkins.
Specialized Fertilizers for Crop-Specific Results
Every crop has its own nutritional requirements, and targeted fertilizer formulas can meet those requirements. Here is a quick summary of some key fertilizer needs by crop:
- Potato fertilizer: High potassium level to develop the tuber and skin quality.
- Corn fertilizer: Nitrogen formulas are designed to get quick vegetative growth and large ears.
- Pumpkin fertilizer: Good balanced phosphorus and potassium for flowering and fruit expansion.
- Cucumber fertilizer: Nitrogen for leaf growth early on; potassium for fruit development later on.
If you select the correct specialty fertilizer, you will benefit from a great crop yield.
Crop-Specific Fertilizer Strategies
Different crops exhibit different nutrient demands based on their growth patterns and yield targets. Choosing the appropriate fertilizer for crops leads to healthy plants, maximized productivity and better quality harvests. Customized fertilization allows farmers to match nutrient sources with the actual needs of each crop variety.
Best Potato Fertilizer for Tuber Growth
Potatoes need a soil profile that has an adequate source of nutrients that can promote the establishment of roots and tubers.
Application Strategies:
- Plant potatoes using a fertilizer high in potassium (K), to have a large and firm tuber formation.
- Use phosphorus (P) at balanced levels - this is essential for early root establishment.
- Use nitrogen (N) at controlled levels - minerals can increase leaf tissue production at the expense of tuber production.
Use granules or slow release sources to have nutrient sources available at the right time.
Top Corn Fertilizer Options for Maximum Yield
Corn is a big feeder of nitrogen and uses a lot of nutrients while growing rapidly in the vegetative (V) phase.
Key fertilization strategies:
- Use a fertilizer high in nitrogen content in any corn fertilizing program to develop strong tall stalks.
- Apply phosphorus early to get the corn root on its feet to develop deep root systems.
- Use side-dressing or fertigation to apply nitrogen to the crop as it peaks.
- Also, some micronutrients like zinc and sulfur can help with kernel development.
Ideal Pumpkin Fertilizer for Bigger Fruits
Pumpkins require adequate nutrient balance to develop sprawling vines and large fruits.
Key Fertilizer Strategies:
- When using pumpkin fertilizer, it should have enough potassium to have high fruit size and skin quality.
- Phosphorus helps to have healthy flowering for fruit set.
- Nitrogen is beneficial in early season to foliage growth but should be reduced as the fruit grows on the vine.
- Organic compost works well with sustained release of nutrients replenishing the soil preserve throughout the season.
Effective Cucumber Fertilizer for Steady Harvests
Cucumbers do best with steady feed as they go through a long fruiting cycle.
Fertilizer Strategies:
- Cucumber fertilizers that are high in nitrogen are good for vegetative growth and early flowering.
- Increase potassium once fruiting begins to maximize flavor, size, and appearance.
- Liquid nutrients include nutrient levels evenly through a fertigation system.
- Balanced micronutrients like calcium will fight off common issues like blossom-end rot.
How to Identify What Your Soil Needs: Soil Testing for Fertilizer for Crops
Soil testing is the first and most important step to follow before using any fertilizer for crops. If you do not know your soil's current nutrient levels, then you may risk over- or under-fertilizing your fields. Soil testing allows farmers to have a clearer picture of pH, macronutrients (N-P-K), and micronutrient availability to help them plan their fertilizer application properly.
Using Soil Tests to Guide Fertilizer Selection
A soil test report indicates which nutrients are deficient, making your fertilizer decisions easier for each crop.
Key Points:
- High nitrogen -Stronger corn fertilizer blends.
- Low potash- Increase potato fertilizer and pumpkin fertilizer applications.
- Low phosphate- Essential for early root growth in all crops.
- Nutrients all balanced- Avoid hidden deficiencies negatively influencing yield.
Spotting Deficiencies Before Planting Crops
If a nutrient deficiency is detected early, it allows for proactive management.
Common inconsistencies to watch for:
- Poor seedling growth may be due to a lack of nitrogen (particularly for corn fertilizer needs).
- Weak root systems indicate phosphorus (very important for potato fertilizer).
- Yellowing leaves may indicate potassium or magnesium problems and is often seen with cucumber fertilizer and pumpkin fertilizer crop.
- Soil testing will help to find these deficiencies before an issue becomes visible.
Matching Fertilizer Type to Soil Condition
The selection of fertilizer is largely reliant upon the composition of the soil.
Tips for Matching Fertilizers:
- Sandy soils more easily lose nutrients - may use slow-release fertilizers to benefit crops.
- Clay soils maintain nutrients longer - need to be monitored and prevented from over-fertilizing.
- Organic matter or organic matter improved nutrient balance - great condition when compost meat is used with pumpkin fertilizer or cucumbers fertilizer.
Saline or alkaline soils can require specialty fertilizers to maintain balance.
Sustainable Fertilizer for Crops: Balancing Yield with Environmental Protection
While fertilizers for crops provide an important role in maximizing crop yields, they can also impact on the surrounding environment if not used properly, which may take years or more to remedy. Sustainable applications of fertilizers allow us the opportunity to provide current food needs, while protecting soil health and water quality, as well as future yields from agriculture. Sustainable fertilization practices are not only about maximizing the efficiency of how plants are fed but also minimizing any adverse impacts to the ecosystems surrounding them.
Reducing Fertilizer Runoff & Water Pollution
Fertilizer, in excess of what plants can use, can leach into water bodies causing pollution and algal blooms. Careful management when applying fertilizer can help mitigate this risk.
Strategies to Reduce Runoff:
- Apply corn and potato fertilizers during dry, calm weather to prevent runoff.
- Use slow release fertilizers that supply nutrients over time.
- Create buffer zones and use grass waterways around fields to allow collection of excess nutrients.
- Do not over-irrigate when using cucumber fertilizers for fertigation systems.
Organic Fertilizers and Biofertilizers for Eco-Friendly Farming
Organic and biofertilizers are natural, sustainable solutions that foster long-lasting soil wellness.
Main Eco-Friendly Options:
- Organic fertilizer for crops, enhances soil structure and microbial activity.
- Biofertilizers (with beneficial bacteria and fungi) not only fix nitrogen as well as release phosphorus.
- Perfect for vegetables! Such as pumpkin fertilizer and cucumber fertilizer that benefit from enhanced soil microbiology.
- Less chance of soils degrading or causing build-up on the chemicals.
Long-Term Soil Conservation Through Responsible Fertilization
Saving soil is critical for the future of farming, and with proper management of fertilizers, fertility can be sustained for decades.
Soil conservation practices:
- Crop rotation is essential to equalize nutrient consumption — for example, follow heavy nitrogen cropping such as corn fertilizer with legumes.
- Utilizing cover crops provides a natural source of nutrient replacement.
- Precision agriculture establishes where to place fertilizer, only supplying the minimum amount of fertilizer for the crops required.
- Regular soil testing keeps your nutrient components in balance while avoiding excess in your soil profile.
FAQ
Q1 Why is fertilizer for crops essential in farming?
Fertilizer for crops supplies essential nutrients to maximize plant growth and increase yield efficiently.
Q2 What is the best potato fertilizer?
The best potato fertilizer contains high potassium and balanced phosphorus for strong tuber development.
Q3 How much nitrogen does corn fertilizer require?
Corn fertilizer typically requires 150-200 lbs of nitrogen per acre, depending on soil test results and crop needs.
Q4 What kind of pumpkin fertilizer works best?
Pumpkin fertilizer should be rich in potassium and phosphorus to support large fruit development and strong vines.
Q5 How often should I apply cucumber fertilizer?
Cucumber fertilizer is best applied every 10-14 days during fruiting, with balanced nitrogen and potassium.
Q6 How do I know which fertilizer type my soil needs?
Conduct a soil test to determine nutrient deficiencies and select the right fertilizer for crops accordingly.
Conclusion: Choose the Right Fertilizer for Crops to Secure Higher Yields and Sustainable Growth
Choosing the right fertilizers for crops is tied to crop yields and the sustainability and health of the farming. Every crop has its own nutritional desires, and by having a plan on how to fertilize and what fertilizers will be best, these nutritional desires can be satisfied.
For potatoes, the fertilizer is almost exclusively potassium and phosphorus to promote tuber growth. Corn fertilizer requires high nitrogen levels for the speedy vegetative growth. Pumpkins will call for a balanced fertilizer to promote both vine and fruit sizing. Cucumber fertilizers will almost exclusively be N-P-K fertilizers of some sort, and feeding crops regularly with K can produce consistent yields.
Combining soil testing, personalized fertilization programs, and environmentally friendly working can help farmers produce crops and protect farmers. If a grower understands the needs for a crop, knows what types of fertilizers can help fit those needs, and then applies fertilizers responsibly, they can be able to produce a profit and keep their farms soil healthy for many years.





